Purposes
Basic use
Hand-held binoculars vary from small three × 10 Galilean opera glasses, utilized in theaters, to glasses with 7 to 12 diameters magnification and 30 to 50 mm targets for typical outside use.
Many tourist attractions have put in pedestal-mounted, coin-operated binoculars to permit guests to acquire a more in-depth view of the attraction.
Land Surveys and Geographic Knowledge Assortment
Though know-how has surpassed utilizing binoculars for knowledge assortment, traditionally these have been superior instruments utilized by geographers and different geoscientists. Discipline glasses nonetheless at the moment can present visible assist when surveying massive areas.
Hen watching
Birdwatching is a very talked-about interest amongst nature and animal lovers and a binocular is their most elementary software. Sometimes binoculars with a magnification of 7x to 10x are used.
Searching
Hunters generally use binoculars within the discipline as a strategy to see sport animals which can be too distant to identify with the bare eye. Hunters mostly use 8x binoculars with gentle transmission and enormous sufficient targets to assemble gentle in low gentle situations.
Vary discovering
Many binoculars have a variety discovering reticle (scale) superimposed upon the view. This scale permits the space to the item to be estimated if the item's peak is thought (or estimable). The frequent mariner 7×50 binoculars have these scales with the angle between marks equal to five mil. One mil is equal to the angle between the highest and backside of an object one meter in peak at a distance of 1000 meters.
Subsequently, to estimate the space to an object that could be a recognized peak the formulation is:

the place:
 is the Distance to the item in meters.
is the Distance to the item in meters. is the recognized Object Peak.
is the recognized Object Peak. is the angular peak of the item in variety of Mil.
is the angular peak of the item in variety of Mil.
With the everyday 5 mil scale (every mark is 5 mil), a lighthouse that's three marks excessive that's recognized to be 120 meters tall is 8000 meters distance.

Army
Binoculars have an extended historical past of army use. Galilean designs have been broadly used as much as the tip of the 19th century once they gave strategy to porro prism varieties. Binoculars constructed for basic army use are typically extra rugged than their civilian counterparts. They typically keep away from fragile middle focus preparations in favor of unbiased focus, which additionally makes for simpler, more practical weatherproofing. Prism units in army binoculars could have redundant aluminized coatings on their prism units to ensure they do not lose their reflective qualities in the event that they get moist.
One variant type was referred to as "trench binoculars", a mixture of binoculars and periscope, usually used for artillery recognizing functions. It projected just a few inches above the parapet, thus holding the viewer's head safely within the trench.
Army binoculars of the Cold War period have been generally fitted with passive sensors that detected lively IR emissions, whereas trendy ones often are fitted with filters blocking laser beams used as weapons. Additional, binoculars designed for army utilization could embody a stadiametric reticle in a single ocular with a view to facilitate vary estimation.
There are binoculars designed particularly for civilian and army use at sea. Handheld fashions might be 5× to 7× however with very massive prism units mixed with eyepieces designed to offer beneficiant eye reduction. This optical mixture prevents the picture vignetting or going darkish when the binoculars are pitching and vibrating relative to the viewer's eye. Giant, high-magnification fashions with massive targets are additionally utilized in mounted mountings.
Very massive binocular naval rangefinders (as much as 15 meters separation of the 2 goal lenses, weight 10 tons, for ranging World War II naval gun targets 25 km away) have been used, though late-20th century know-how made this utility redundant.
Astronomical

25 × 150 binoculars tailored for astronomical use
Binoculars are broadly utilized by amateur astronomers; their extensive field of view makes them helpful for comet and supernova in search of (big binoculars) and basic statement (moveable binoculars). Binoculars particularly geared in the direction of astronomical viewing could have bigger aperture targets (within the 70 mm or 80 mm vary) as a result of the diameter of the target lens will increase the whole quantity of sunshine captured, and due to this fact determines the faintest star that may be noticed. Binoculars designed particularly for astronomical viewing (usually 80 mm and bigger) are generally designed with out prisms with a view to enable most gentle transmission. Such binoculars additionally often have changeable eyepieces to fluctuate magnification. Binoculars with excessive magnification and heavy weight often require some type of mount to stabilize the picture. A magnification of 10x is usually thought-about the sensible restrict for statement with handheld binoculars. Binoculars extra highly effective than 15×70 require assist of some kind. A lot bigger binoculars have been made by amateur telescope makers, basically utilizing two refracting or reflecting astronomical telescopes.
Of explicit relevance for low-light and astronomical viewing is the ratio between magnifying energy and goal lens diameter. A decrease magnification facilitates a bigger discipline of view which is helpful in viewing the Milky Way and enormous nebulous objects (known as deep sky objects) such because the nebulae and galaxies. The big (typical 7 mm utilizing 7x50) exit pupil [objective (mm)/power] of those gadgets ends in a small portion of the gathered gentle not being usable by people whose pupils don't sufficiently dilate. For instance, the pupils of these over 50 not often dilate over 5 mm extensive. The big exit pupil additionally collects extra gentle from the background sky, successfully lowering distinction, making the detection of faint objects tougher besides maybe in distant areas with negligible light pollution. Many astronomical objects of eight magnitude or brighter, such because the star clusters, nebulae and galaxies listed within the Messier Catalog, are readily seen in hand-held binoculars within the 35 to 40 mm vary, as are discovered in lots of households for birding, searching, and viewing sports activities occasions. For observing smaller star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies binocular magnification is a vital issue for visibility as a result of these objects seem tiny at typical binocular magnifications.
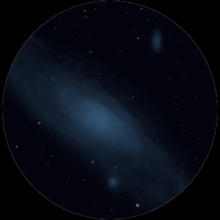
A simulated view of how the
Andromeda galaxy (Messier 31) would seem in a pair of binoculars
Some open clusters, resembling the brilliant double cluster (NGC 869 and NGC 884) within the constellation Perseus, and globular clusters, resembling M13 in Hercules, are simple to identify. Amongst nebulae, M17 in Sagittarius and the North American nebula (NGC 7000) in Cygnus are additionally readily seen. Binoculars can present just a few of the wider-split binary stars resembling Albireo within the constellation Cygnus.
Various photo voltaic system objects which can be largely to fully invisible to the human eye are moderately detectable with medium-size binoculars, together with bigger craters on the Moon; the dim outer planets Uranus and Neptune; the internal "minor planets" Ceres, Vesta and Pallas; Saturn's largest moon Titan; and the Galilean moons of Jupiter. Though seen unaided in pollution-free skies, Uranus and Vesta require binoculars for simple detection. 10×50 binoculars are restricted to an apparent magnitude of +9.5 to +11 relying on sky situations and observer expertise. Asteroids like Interamnia, Davida, Europa and, except below distinctive situations Hygiea, are too faint to be seen with generally bought binoculars. Likewise too faint to be seen with most binoculars are the planetary moons besides the Galileans and Titan, and the dwarf planets Pluto and Eris. Different troublesome binocular targets embody the phases of Venus and the rings of Saturn. Solely binoculars with very excessive magnification, 20x or increased, are able to discerning Saturn's rings to a recognizable extent. Excessive-power binoculars can generally present one or two cloud belts on the disk of Jupiter if optics and observing situations are sufficiently good.





















